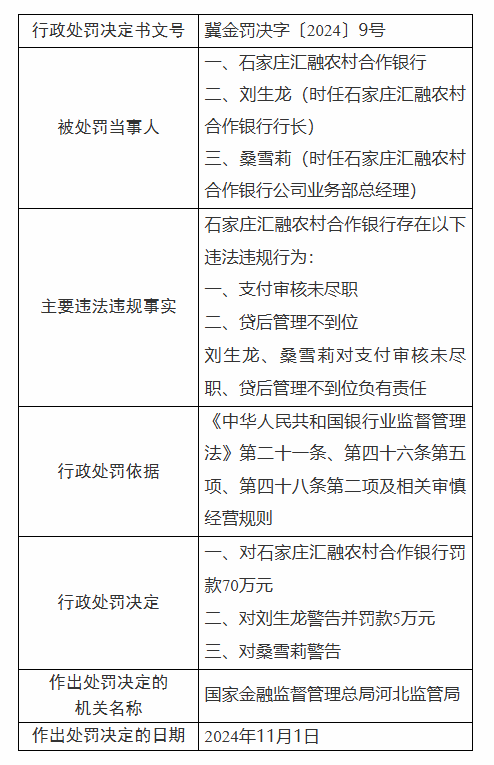
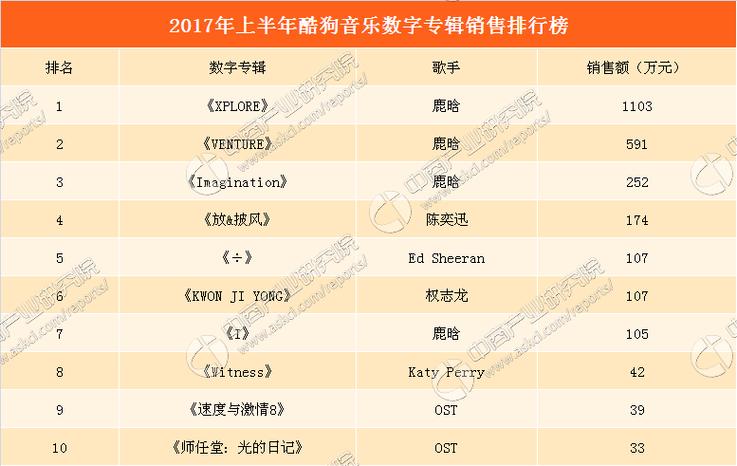
保险公司外勤组织架构图
Effective organizational structure is essential for insurance companies to operate efficiently, manage risk, and deliver highquality services to customers. By defining clear roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines, insurance companies can streamline operations, improve decisionmaking, and adapt to changing market dynamics.
Insurance Company Organizational Structure
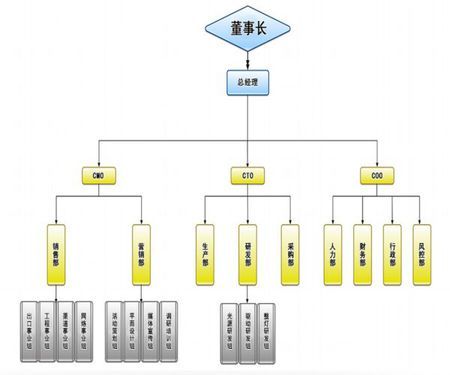
- Customer Service: Providing assistance and support to policyholders, addressing inquiries and concerns.
- Actuarial: Analyzing data to assess risk and set pricing for insurance products.
- CFO (Chief Financial Officer): Oversees financial planning, budgeting, and reporting.
- Sales and Marketing: Acquiring new customers and retaining existing ones through various sales and marketing strategies.
- Claims: Handling claims processing, investigation, and settlements.
The executive leadership team comprises toplevel executives responsible for setting strategic goals, making key decisions, and overseeing overall operations. This includes:
Insurance companies typically have several departments, each focusing on specific functions:
An organizational structure is crucial for any insurance company to effectively manage its operations, resources, and personnel. It defines the hierarchy, roles, and responsibilities within the company, facilitating smooth workflow and decisionmaking processes. Let's delve into the typical organizational structure of an insurance company:
```html
Within each department, there is a hierarchical structure consisting of various roles:
- CTO (Chief Technology Officer): Oversees technology infrastructure and innovation.
- Administrative Staff: Provide administrative support to the department.
- Analysts/Specialists: Responsible for specialized tasks such as underwriting analysis, claims assessment, or actuarial modeling.
```
Some insurance companies may adopt a matrix structure, where employees report to both functional managers (e.g., department heads) and project managers simultaneously. This structure allows for better coordination and communication across departments, especially for crossfunctional projects.
Large insurance companies operating in multiple regions or countries may adopt a geographic structure, with divisions or branches organized based on geographic locations. Each division may have its own set of departments and leadership team to cater to the specific needs of that region.